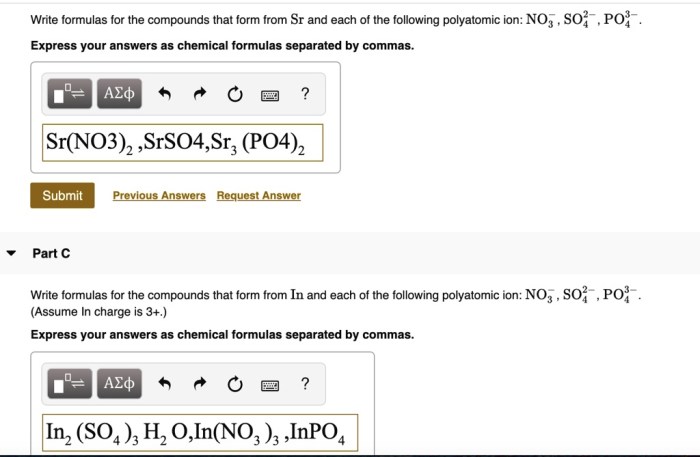
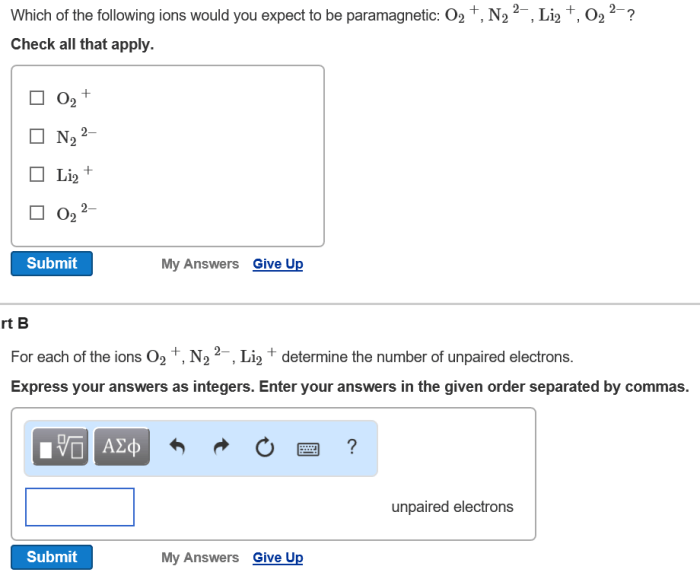
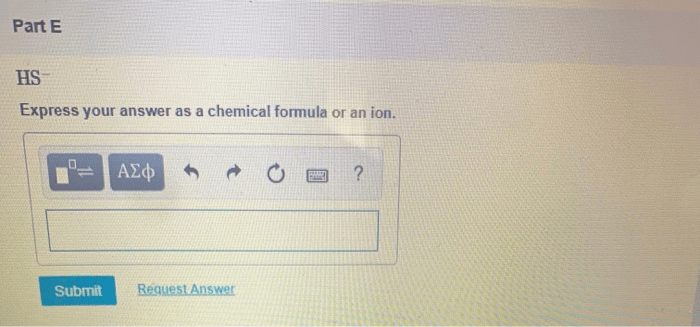
Express your answer as an ion introduces us to the captivating world of ions, the charged particles that play a pivotal role in shaping our existence. From the tiniest atoms to the vast oceans, ions are ubiquitous, influencing everything from biological processes to industrial applications.
Delving into the depths of ion chemistry, we’ll explore the formation, reactions, and equilibrium of these fascinating particles, unlocking their secrets and revealing their profound impact on our world.
Ion Definition and Properties
An ion is an atom or molecule that has lost or gained one or more electrons, resulting in a net electric charge. Ions are classified as either cations or anions, depending on their charge.
Cations are positively charged ions, while anions are negatively charged ions. The loss of electrons results in the formation of cations, and the gain of electrons results in the formation of anions.
Types of Ions
Ions can be classified into two main types: monoatomic ions and polyatomic ions.
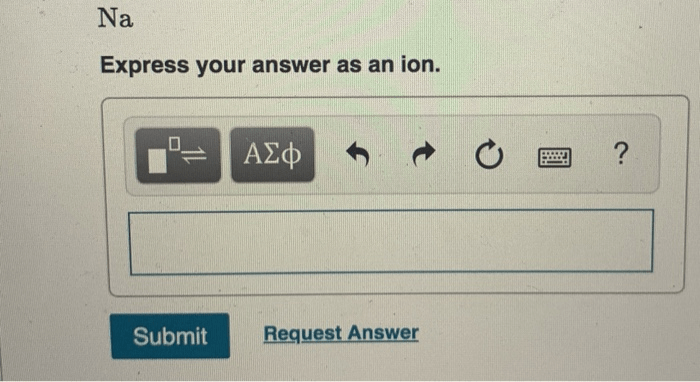
- Monoatomic ionsare formed when a single atom loses or gains electrons. Examples include sodium ions (Na+), chloride ions (Cl-), and calcium ions (Ca2+).
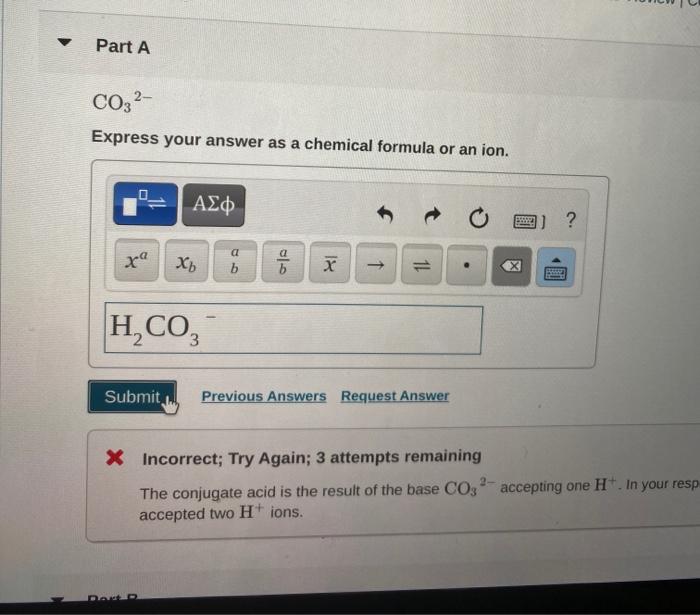
- Polyatomic ionsare formed when a group of atoms loses or gains electrons. Examples include hydroxide ions (OH-), carbonate ions (CO32-), and sulfate ions (SO42-).
Examples of Ions in Everyday Life
Ions are found in many everyday substances, including:
- Table salt (NaCl)contains sodium ions (Na+) and chloride ions (Cl-).
- Baking soda (NaHCO3)contains sodium ions (Na+), hydrogen ions (H+), carbonate ions (CO32-), and hydroxide ions (OH-).
- Vinegar (CH3COOH)contains hydrogen ions (H+) and acetate ions (CH3COO-).
Ion Formation and Reactions
Ion formation is a crucial process that involves the gain or loss of electrons by atoms or molecules. This transformation results in the creation of electrically charged particles known as ions.
Electron Involvement in Ion Formation
Electrons play a pivotal role in ion formation. When an atom loses one or more electrons, it becomes positively charged, forming a cation. Conversely, when an atom gains electrons, it becomes negatively charged, forming an anion.
Types of Ion Reactions
Ions can undergo various types of reactions, including:
- Neutralization reactions:Occur between an acid and a base, resulting in the formation of salt and water.
- Precipitation reactions:Involve the formation of an insoluble solid precipitate when two ions in solution combine.
- Redox reactions:Transfer electrons between reactants, resulting in changes in oxidation states.
Ion Concentration and Equilibrium: Express Your Answer As An Ion
Ion concentration refers to the number of ions present in a given volume of solution. It is a crucial factor in understanding the behavior and properties of ionic solutions. Several factors can affect ion concentration, including temperature, solvent, and the presence of other ions.
Factors Affecting Ion Concentration
- Temperature:As temperature increases, the kinetic energy of ions increases, causing them to move faster and collide more frequently. This increased collision rate leads to a decrease in ion concentration.
- Solvent:The nature of the solvent can influence ion concentration. Solvents with high dielectric constants, such as water, favor the dissociation of ions, leading to higher ion concentrations.
- Presence of Other Ions:The presence of other ions in a solution can affect ion concentration through a phenomenon known as the common ion effect. When an ion is added to a solution that already contains the same ion, the concentration of the added ion decreases.
Equilibrium State of Ions in a Solution
In a solution, ions are constantly undergoing dissociation and recombination reactions. At equilibrium, the rate of dissociation equals the rate of recombination, resulting in a constant ion concentration. The equilibrium state of ions is influenced by factors such as temperature, pressure, and the presence of other ions.
“At equilibrium, the net change in ion concentration over time is zero.”
Understanding ion concentration and equilibrium is essential for various applications, including electrochemistry, analytical chemistry, and biological processes.
Expressing your answer as an ion can be quite straightforward. Take the example of elevator in Britain . This can be easily expressed as the ion “lift”, which is the term used in Britain for an elevator. Expressing your answer as an ion can thus be a simple and effective way to convey your thoughts.
Ion Applications
Ions are not only crucial in biological processes but also find applications in various fields, including medicine, industry, and research.
Medical Applications
- Ionizing radiation therapy uses ions to target and destroy cancer cells.
- Ions are used in medical imaging techniques like X-rays and CT scans.
- Electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium ions, are essential for maintaining fluid balance and nerve function.
Industrial Applications
- Electroplating uses ions to coat metals with a protective or decorative layer.
- Ion exchange resins are used in water treatment and purification processes.
- Fuel cells rely on ion exchange reactions to generate electricity.
Biological Processes, Express your answer as an ion
- Ion channels in cell membranes regulate the flow of ions, which is essential for nerve impulses and muscle contractions.
- Ions are involved in enzyme catalysis, where they stabilize the transition state and facilitate chemical reactions.
- Ion gradients across cell membranes provide the driving force for active transport, a process that moves molecules against their concentration gradient.
FAQs
What is an ion?
An ion is an atom or molecule that has lost or gained electrons, resulting in a net electrical charge.
How are ions formed?
Ions are formed when an atom or molecule loses or gains electrons, altering its electron configuration.
What are the different types of ions?
Ions can be classified as cations (positively charged) or anions (negatively charged).