Embark on a journey into the realm of matter, where we unravel the intricacies of substances and mixtures through our matter-substances vs mixtures answer key. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamental concepts that distinguish these two categories, providing a solid foundation for understanding the composition and properties of the world around us.
Delving deeper, we explore the unique characteristics of substances, their fixed composition, and definite properties. In contrast, we examine the variable nature of mixtures, their diverse compositions, and the fascinating interplay of their components. The discussion culminates in a comprehensive understanding of the methods employed to separate substances from mixtures, empowering us with the knowledge to manipulate and utilize these materials effectively.
Definitions
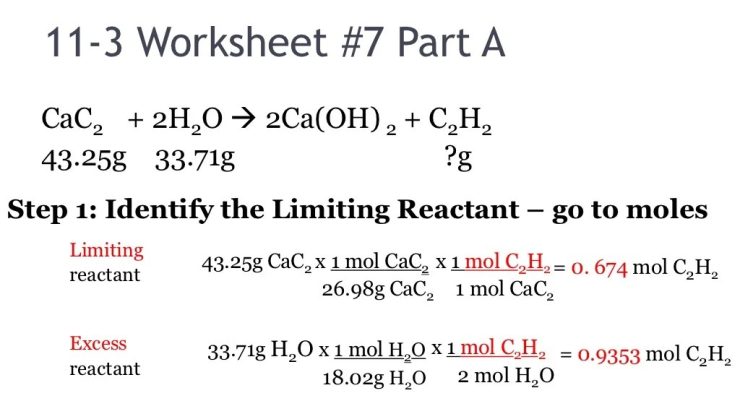
Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. It exists in two primary classifications: substances and mixtures.
A substance is a pure chemical compound with a definite composition and specific properties. Examples include water (H2O), salt (NaCl), and gold (Au).
A mixture is a combination of two or more substances that retain their individual properties. Examples include saltwater (a mixture of water and salt), air (a mixture of gases), and granite (a mixture of minerals).
Properties of Substances: Matter-substances Vs Mixtures Answer Key
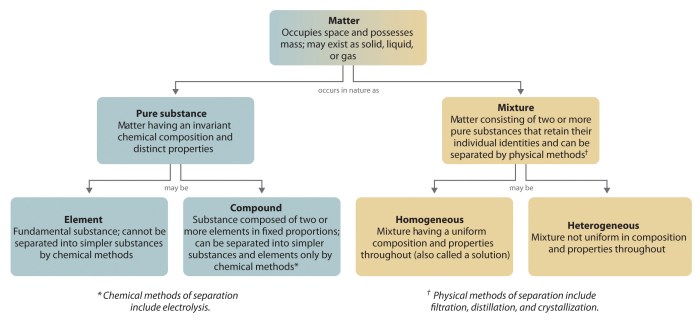
Substances are characterized by their fixed composition and definite properties.
Fixed composition means that the proportions of the elements or molecules in a substance are always the same. For example, water is always composed of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom (H2O).
Definite properties means that the physical and chemical properties of a substance are always the same. For example, water always has a freezing point of 0°C and a boiling point of 100°C.
Properties of Mixtures
Mixtures are characterized by their variable composition and properties.
Variable composition means that the proportions of the components in a mixture can vary. For example, saltwater can have different concentrations of salt depending on how much salt is dissolved in the water.
Variable properties means that the physical and chemical properties of a mixture can vary depending on the composition of the mixture. For example, the freezing point of saltwater decreases as the concentration of salt increases.
Helpful Answers
What is the primary distinction between substances and mixtures?
Substances possess a fixed composition and definite properties, while mixtures exhibit variable composition and properties.
How can we separate substances from mixtures?
Techniques such as filtration, distillation, and chromatography are commonly employed to separate substances based on their physical properties.
What are some real-world examples of substances and mixtures?
Pure water is an example of a substance, while saltwater is a mixture of water and salt.