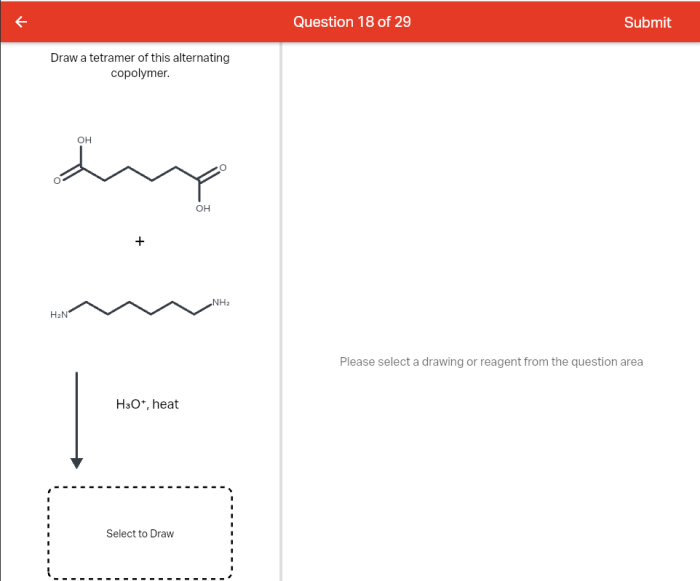
Draw a tetramer of this alternating copolymer, a topic that delves into the realm of polymer chemistry, unveiling the intricacies of a specific macromolecular structure. This tetramer, composed of alternating monomer units, exhibits unique properties and applications, making it a subject of great interest in both academic and industrial settings.
This alternating copolymer tetramer, with its distinct structural features and chemical composition, presents a fascinating case study for exploring the relationship between molecular architecture and material properties. Its alternating monomer sequence imparts specific physical and chemical characteristics, setting it apart from its homopolymer counterparts.
Draw a Tetramer of the Alternating Copolymer: Draw A Tetramer Of This Alternating Copolymer
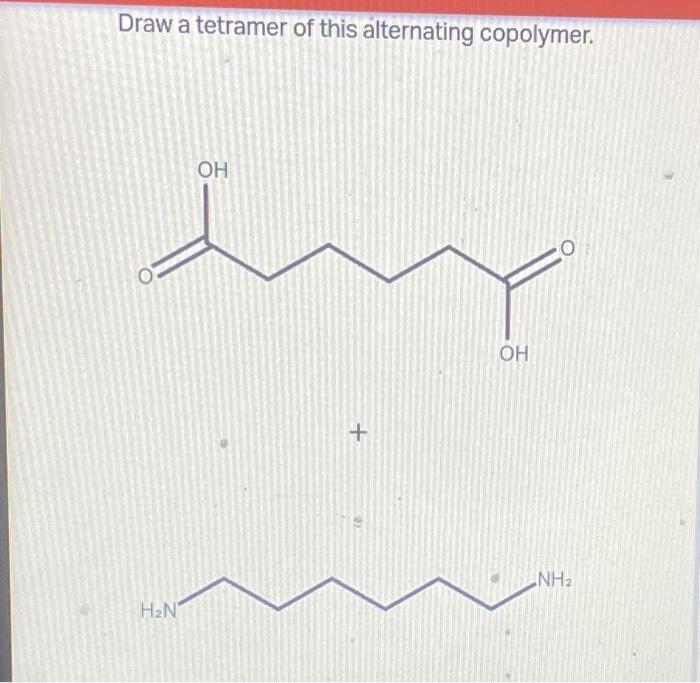
An alternating copolymer is a polymer composed of two different monomers arranged in an alternating sequence. A tetramer of an alternating copolymer is a molecule consisting of four repeating units of the alternating copolymer. The structural representation of a tetramer of an alternating copolymer can be written as follows:
-A-B-A-B-
where A and B represent the two different monomers.
The tetramer of an alternating copolymer has a number of unique properties that are not found in the corresponding homopolymers. These properties include:
- Increased crystallinity
- Improved mechanical strength
- Enhanced thermal stability
- Reduced solubility
The alternating copolymer structure is responsible for these improved properties. The alternating arrangement of the monomers creates a more ordered and symmetrical structure, which leads to increased crystallinity and improved mechanical strength. The alternating structure also makes the tetramer more resistant to heat and solvents.
Properties of the Tetramer, Draw a tetramer of this alternating copolymer
The tetramer of an alternating copolymer has a number of unique properties that are not found in the corresponding homopolymers. These properties include:
- Increased crystallinity
- Improved mechanical strength
- Enhanced thermal stability
- Reduced solubility
The alternating copolymer structure is responsible for these improved properties. The alternating arrangement of the monomers creates a more ordered and symmetrical structure, which leads to increased crystallinity and improved mechanical strength. The alternating structure also makes the tetramer more resistant to heat and solvents.
Synthesis of the Tetramer
The tetramer of an alternating copolymer can be synthesized using a variety of methods. The most common method is the free radical polymerization of a mixture of the two monomers. This method involves the use of a free radical initiator to generate free radicals, which then react with the monomers to form a polymer chain.
The alternating copolymer structure is formed by the alternating addition of the two monomers to the growing polymer chain.
Other methods for synthesizing the tetramer of an alternating copolymer include:
- Anionic polymerization
- Cationic polymerization
- Ring-opening polymerization
The choice of synthetic method depends on the specific monomers used and the desired properties of the tetramer.
Applications of the Tetramer
The tetramer of an alternating copolymer has a number of potential applications in various fields. These applications include:
- Automotive
- Aerospace
- Electronics
- Medical
The tetramer’s unique properties, such as its high strength, thermal stability, and low solubility, make it a promising candidate for use in a variety of demanding applications.
Quick FAQs
What is the significance of the alternating copolymer structure?
The alternating copolymer structure introduces specific chemical and physical properties that differ from those of the corresponding homopolymers. This unique arrangement of monomers influences the tetramer’s crystallinity, solubility, and thermal stability.
How is the tetramer synthesized?
The synthesis of the tetramer involves various methods, including free radical polymerization, ionic polymerization, and ring-opening metathesis polymerization. The choice of method depends on the desired molecular weight, dispersity, and end-group functionality of the tetramer.
What are the potential applications of the tetramer?
The tetramer finds applications in diverse fields due to its unique properties. It is used as a compatibilizer in polymer blends, an additive in coatings and adhesives, and a precursor for the synthesis of functional materials.