Substrates products and other participants involved in transcription – As substrates, products, and other participants involved in transcription take center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with authoritative knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
The complex and multifaceted process of transcription, a fundamental step in gene expression, relies on a delicate interplay between various substrates, products, and participants. This introductory paragraph sets the stage for an in-depth exploration of each of these elements, their roles, and their interactions.
Substrates Involved in Transcription
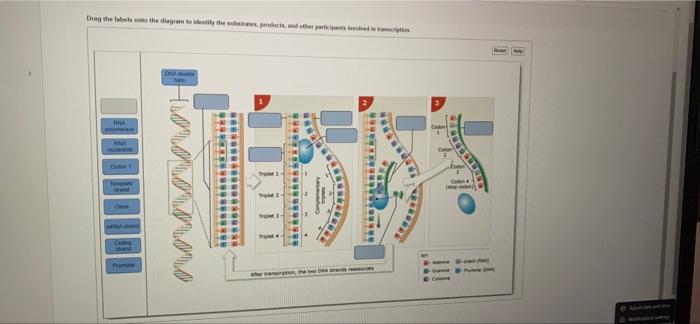
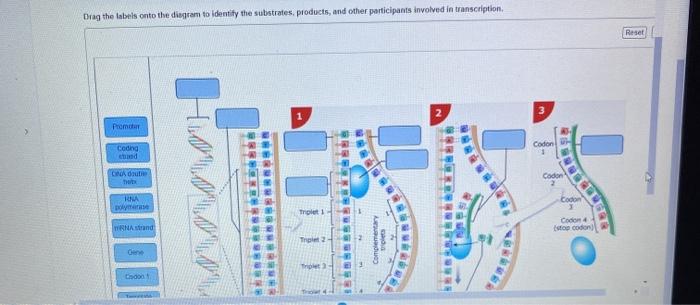
Transcription is the process of copying a gene’s DNA sequence into a complementary RNA molecule. The substrates involved in transcription are DNA, RNA nucleotides, and RNA polymerase.
- DNA:The DNA molecule contains the genetic information that is transcribed into RNA.
- RNA nucleotides:The four RNA nucleotides (adenine, cytosine, guanine, and uracil) are used to build the RNA molecule.
- RNA polymerase:RNA polymerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transcription process.
Products of Transcription
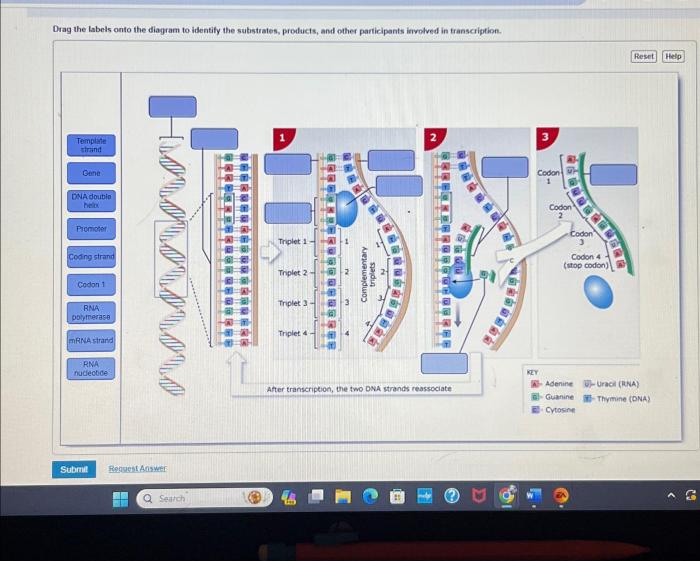
The products of transcription are mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA.
- mRNA (messenger RNA):mRNA carries the genetic information from the DNA to the ribosomes, where it is used to direct protein synthesis.
- tRNA (transfer RNA):tRNA molecules carry amino acids to the ribosomes, where they are incorporated into proteins.
- rRNA (ribosomal RNA):rRNA molecules are components of ribosomes, the cellular structures where protein synthesis occurs.
Other Participants Involved in Transcription: Substrates Products And Other Participants Involved In Transcription
In addition to the substrates, several other participants are involved in transcription. These include:
- Transcription factors:Transcription factors are proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences and regulate the transcription of genes.
- Enhancers:Enhancers are DNA sequences that bind to transcription factors and help to increase the rate of transcription.
- Silencers:Silencers are DNA sequences that bind to transcription factors and help to decrease the rate of transcription.
Comparison of Substrates, Products, and Participants
The following table compares the substrates, products, and other participants involved in transcription:
| Type of Molecule | Role in Transcription | Other Information |
|---|---|---|
| DNA | Template for RNA synthesis | Double-stranded molecule |
| RNA nucleotides | Building blocks of RNA molecules | Four types: adenine, cytosine, guanine, uracil |
| RNA polymerase | Catalyzes the transcription process | Multi-subunit enzyme |
| mRNA | Carries genetic information to ribosomes | Single-stranded molecule |
| tRNA | Carries amino acids to ribosomes | Single-stranded molecule |
| rRNA | Components of ribosomes | Single-stranded molecule |
| Transcription factors | Regulate the transcription of genes | Proteins that bind to DNA |
| Enhancers | Increase the rate of transcription | DNA sequences that bind to transcription factors |
| Silencers | Decrease the rate of transcription | DNA sequences that bind to transcription factors |
Regulation of Transcription
Transcription is a highly regulated process. The rate of transcription is controlled by a variety of factors, including:
- Transcription factors:Transcription factors can bind to DNA and either promote or inhibit transcription.
- Enhancers:Enhancers are DNA sequences that bind to transcription factors and help to increase the rate of transcription.
- Silencers:Silencers are DNA sequences that bind to transcription factors and help to decrease the rate of transcription.
- Chromatin structure:The structure of chromatin can affect the accessibility of DNA to transcription factors.
- Environmental factors:Environmental factors, such as temperature and pH, can also affect the rate of transcription.
Applications of Transcription
Transcription is a fundamental process in molecular biology. It is used in a variety of applications, including:
- Gene expression analysis:Transcription can be used to measure the expression of genes.
- Protein production:Transcription is used to produce proteins for therapeutic purposes.
- Diagnosis and treatment of diseases:Transcription can be used to diagnose and treat diseases.
Query Resolution
What are the key substrates involved in transcription?
The primary substrate in transcription is DNA, which serves as the template for RNA synthesis.
What are the main products of transcription?
The primary product of transcription is messenger RNA (mRNA), which carries the genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes for protein synthesis.
Who are the key participants involved in transcription?
The key participants in transcription include RNA polymerase, transcription factors, and regulatory proteins.