Free omental flap with microvascular anastomosis, a surgical technique that involves transferring a portion of the omentum to a recipient site, has emerged as a promising approach in reconstructive surgery. This innovative procedure offers unique advantages and has gained significant attention in the medical field.
As we delve into the intricacies of this technique, we will explore its indications, surgical approach, postoperative management, outcomes, and potential applications. This comprehensive guide will provide a thorough understanding of free omental flap with microvascular anastomosis, empowering healthcare professionals to make informed decisions and optimize patient outcomes.
Definition of Free Omental Flap with Microvascular Anastomosis
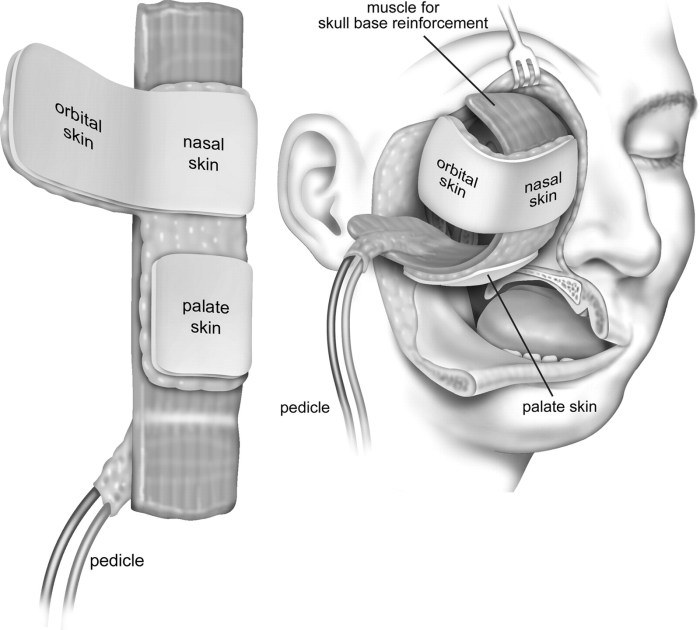
A free omental flap is a surgical procedure that involves harvesting a portion of the omentum, a fatty apron-like structure that hangs from the stomach, and transferring it to another part of the body to restore lost or damaged tissue.
Microvascular anastomosis is a surgical technique that involves connecting tiny blood vessels under a microscope to ensure the survival of the transplanted tissue.
Indications for Free Omental Flap with Microvascular Anastomosis
Free omental flap with microvascular anastomosis is indicated for a variety of reconstructive procedures, including:
- Breast reconstruction after mastectomy
- Head and neck reconstruction after tumor resection
- Limb salvage after trauma or infection
- Pelvic floor reconstruction
Advantages of free omental flap compared to other reconstructive techniques include its large size, pliable nature, and abundant blood supply.
Surgical Technique: Free Omental Flap With Microvascular Anastomosis
The surgical technique for free omental flap with microvascular anastomosis involves the following steps:
- Harvesting the omental flap: The omentum is carefully dissected and removed from the abdominal cavity, preserving its blood supply.
- Recipient site preparation: The area where the flap will be transplanted is prepared to receive the blood vessels.
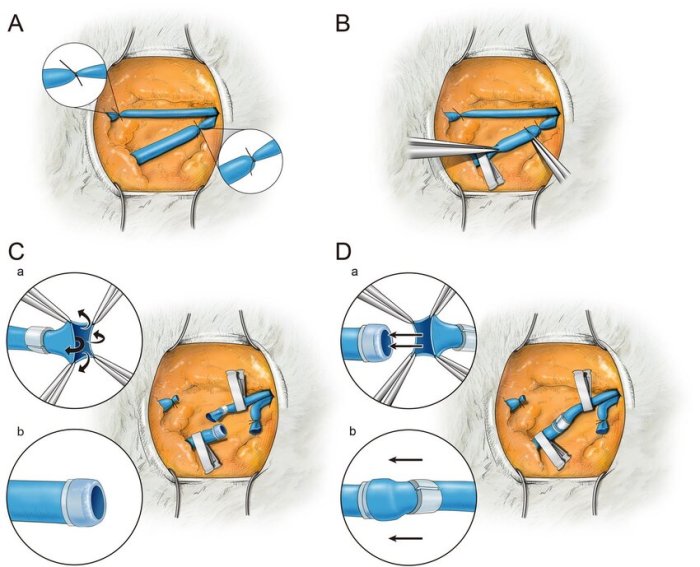
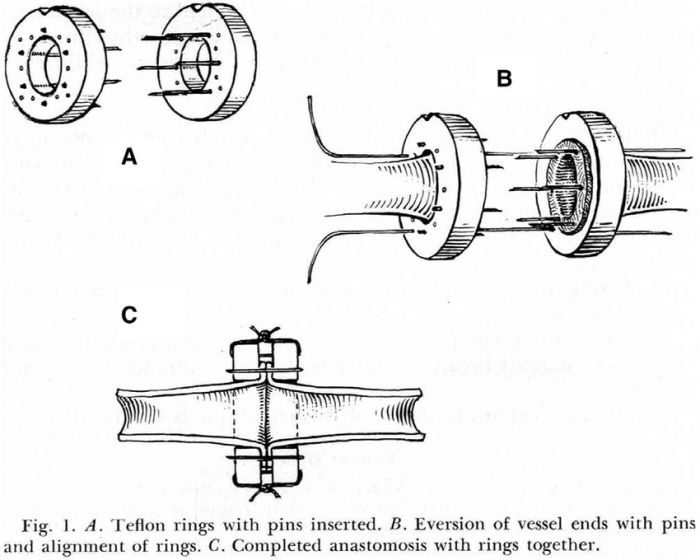
- Microvascular anastomosis: The blood vessels of the flap are connected to the blood vessels of the recipient site using microsurgical techniques.
- Flap inset: The flap is positioned and secured in the recipient site.
Potential risks and complications of the procedure include bleeding, infection, flap necrosis, and thrombosis.
Postoperative Management
Postoperative care for patients who have undergone free omental flap with microvascular anastomosis includes:
- Monitoring vital signs and flap perfusion
- Antibiotic therapy to prevent infection
- Anticoagulant therapy to prevent blood clots
- Regular follow-up appointments to assess healing and monitor for complications
Outcomes and Prognosis
The success rate of free omental flap with microvascular anastomosis is generally high, with a reported survival rate of over 90%. Long-term outcomes are variable and depend on factors such as the underlying medical condition, surgical expertise, and patient compliance.
Case studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of free omental flap in restoring function and improving quality of life in patients with complex reconstructive needs.
FAQ Section
What are the primary indications for free omental flap with microvascular anastomosis?
Free omental flap with microvascular anastomosis is commonly indicated for reconstructing complex tissue defects in various areas of the body, including the head and neck, trunk, and extremities. It is particularly useful in situations where conventional reconstructive techniques are not feasible or have failed.
What are the advantages of free omental flap over other reconstructive techniques?
Free omental flap offers several advantages over other reconstructive techniques. It provides a large, well-vascularized tissue source with minimal donor site morbidity. The omentum’s versatility allows for its use in a wide range of reconstructive applications. Additionally, the microvascular anastomosis technique ensures reliable blood flow to the transplanted tissue, promoting successful flap survival and integration.
What are the potential risks and complications associated with free omental flap with microvascular anastomosis?
As with any surgical procedure, free omental flap with microvascular anastomosis carries potential risks and complications. These may include bleeding, infection, flap failure, and thrombosis of the microvascular anastomosis. Careful patient selection, meticulous surgical technique, and diligent postoperative care are crucial to minimize these risks.